By Kesaobaka Pelokgale
As citizens of Botswana, we have always been proud of our country’s stable government and thriving economy. Central to its economic resilience is the prudent management of foreign reserves, which plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the country’s financial stability and supporting its economic growth trajectory.. In this short read, we explore why these reserves are so vital for the country’s prosperity.
The Story Behind Botswana’s Foreign Reserves

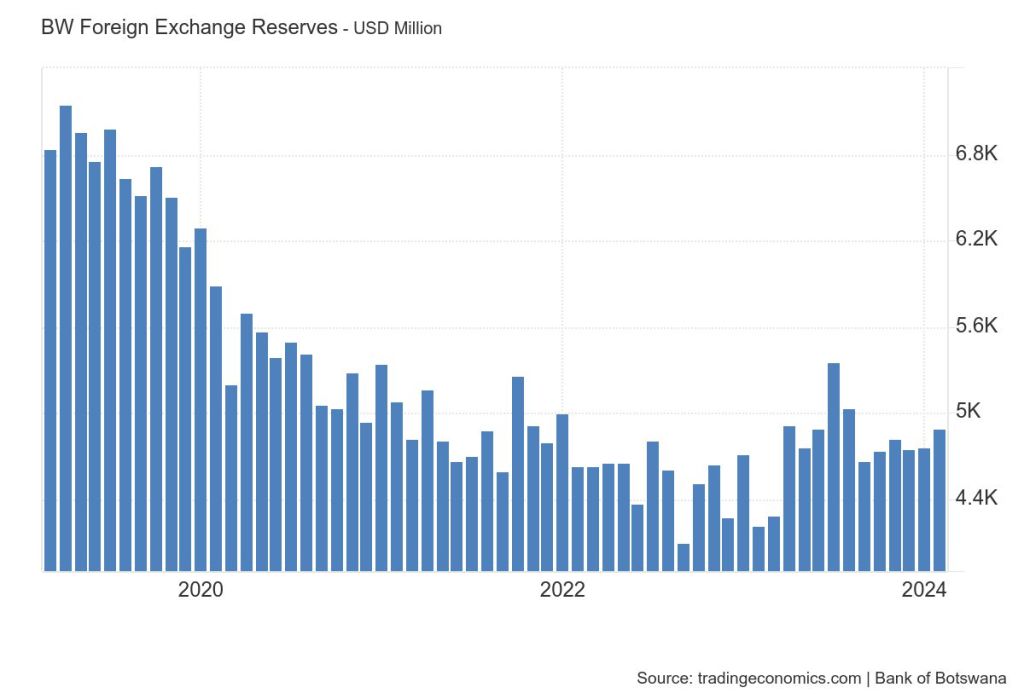
Since gaining independence in 1966, Botswana has strategically leveraged its abundant diamond resources to build robust foreign reserves. It is important to note that the foreign reserves are not solely dependent on diamonds. While diamonds and other minerals have historically been a major contributor, revenue from other sectors tourism, agriculture, and services also plays a significant role. Therefore, Botswana’s foreign reserves are the result of a diverse range of economic activities and sources of income. The government, through the Bank of Botswana, has implemented sound policies to manage these reserves effectively, ensuring their availability to weather economic uncertainties and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Why Foreign Reserves Matter

Think of foreign reserves as a savings account for a country. They serve as a cornerstone of Botswana’s economic stability by providing a cushion against external shocks and fluctuations. They bolster confidence in the national currency, the Botswana pula (BWP), and facilitate smooth trade and investment transactions, thereby fostering sustained economic growth. To explain this in more simple terms:
- When Botswana sells a lot of its resources, it gets more money in foreign reserves. This makes the country’s money stronger, so things aren’t too expensive for people.
- If Botswana imports more than it exports (buys more from other countries than it sells), it uses foreign reserves to pay for the difference. This helps keep prices stable and ensures everyone can buy the things they need.
- Foreign reserves also help when the economy isn’t doing well. For example, if there’s a global economic crisis, Botswana can use its reserves to keep the economy going and make sure people have jobs.
How Foreign Reserves Help the Economy and Ordinary Motswana

When a country maintains adequate foreign reserves:
- They act as a financial buffer, helping stabilize the prices of essential goods like food and clothing, which ensures affordability for citizens.
- They contribute to a stable financial environment, allowing banks to offer loans at reasonable interest rates, thereby facilitating access to credit for individuals looking to purchase homes or start businesses.
- They provide the government with funds for strategic investments in critical infrastructure such as schools and hospitals, improving overall quality of life for citizens.
Challenges and Considerations in Managing Foreign Reserves

Despite their importance, managing foreign reserves poses challenges, including the risk of depletion, balancing short-term needs with long-term objectives, and ensuring transparency and accountability in their management. Botswana must navigate these challenges with prudence and foresight to safeguard its economic stability and prosperity.

Foreign reserves are like a safety blanket for our economy. They help keep the country stable and growing, even when times are tough. By saving and managing its foreign reserves wisely, Botswana can continue to thrive and provide a better future for its people.
